What is muscle gain?
Muscle gain commonly referred to as ‘hypertrophy’ — is the development of mass, density, shape, and function of muscle cells.
What causes muscle gain?
Muscle gain occurs from a combination of exercise stimulus and aligned individualised nutrition intake. Consistent resistance exercise stimulates muscle protein synthesis which effectively, is the body’s way of building muscle as a response to exercise. Muscle gain is supported by our nutrition intake through a variety of factors such as being in an anabolic state (consuming more calories than we expend), meeting our macronutrient requirements (carbohydrates, fat and protein) and consuming foods that are of high nutrient quality.

Does protein intake matter?
Yes, for muscle gain to occur we need to build more muscle than we’re breaking down. Muscle gain requires the rate of muscle protein synthesis to exceed the rate of muscle protein breakdown. Resistance training aids muscle protein synthesis and so does our dietary protein intake, which should be at 1.6-2.0 grams of protein/kg of bodyweight to support the adaptation required for muscle gain.
Is muscle mass important?
From a performance perspective, improvements in lean muscle mass can be linked to key sporting physical indicators such as strength, power to weight ratio and sprint times etc. However, whether or not an athlete should target muscle gain should be determined on an individual basis and factors such as the time of season, individual sport demands and past body-composition history should be considered. It would be advisable to consult a performance nutritionist and ensure you have the correct strength and conditioning programme to ensure you can reach your goal.
From a health perspective, advancing age is associated with a loss of muscle mass, also known as sarcopenia. Therefore, preserving or increasing lean muscle mass would be an important goal to improve life quality and mobility.
From a subjective perspective, a key season people do target muscle gain is for subjective visually improvements to their body shape, tone and appearance.
What steps should I take now to gain muscle mass?
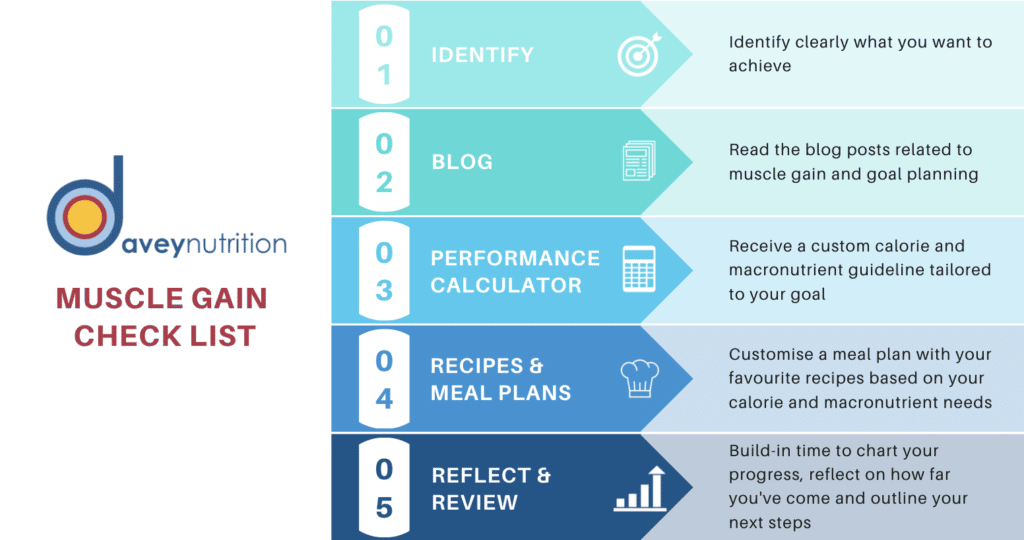
Key Articles To Help You With Muscle Gain
We encourage you to have a read of the following articles:
A framework of nutrition for achieving a health or performance goal – This article will give you actionable steps to put in place a plan to achieve your goal. It will give you a framework to assess your nutrition on a daily or weekly basis to keep you on track and understand what to prioritise.
Body composition changes in the off-season – This article will give you 10 fundamental tips for how to get the basics right, such as getting a quality source of protein at each of your main meals.
The Role of Carbohydrates for Building Muscle Mass – From this article you will receive a clear understanding of how carbohydrates should align with your goal of gaining muscle mass. This article also outlines four nutrition pitfalls you should avoid when trying to gain muscle mass.
A high-performance lifestyle – 10 sustainable habits to adopt to help you achieve your body composition goal.

Top Tips When Using The Performance Calculator For Muscle Gain:
1. Adjust the protein intake between 1.6 – 2.0 grams per kilogram of bodyweight
2. Select “Build lean mass (10% surplus)” if you have time on your side this option will allow you to put on quality lean muscle mass
3. Select “Hard gainer (15% surplus)” if you would like to put on mass quickly
4. Use your calorie and macronutrient information to select a meal plan such as:
MUSCLE GAIN 2600 CALORIE PLAN
MUSCLE GAIN 3000 CALORIE PLAN
MUSCLE GAIN 3400 CALORIE PLAN
Recipes
You will find the following recipes filters useful for the goal of muscle gain: “High-Calorie, High Protein” “Meal Prep” “Muscle Gain” “Quick and Easy” “Recovery Meal”
Check out the following high-protein tasty recipes
Breakfast:
Poached Eggs with Avocado and Smoked Salmon
Flaxseed Porridge with Cacao Nibs
Satisfying Breakfast Smoothie
Snacks:
Chocolate Chip Protein Bars
Banana Recovery Smoothie
Tummy Loving Chia Pudding
Dinners:
Sweet Potato Lasagne
Plant Power Buddha Bowl
Cajun Salmon Burrito Bowl
There are answers to most commonly asked questions on the FAQ page. Please do not hesitate to contact one of your dedicated Nutritionist via the Live Chat on the website or by emailing expertsupport@daveynutrition.com
References:
Campbell, B., Kreider, R., Ziegenfuss, T., La Bounty, P., Roberts, M., Burke, D., Landis, J., Lopez, H. and Antonio, J., 2007. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: protein and exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 4(1), p.8.
Jäger R, Kerksick CM, Campbell BI, Cribb PJ, Wells SD, Skwiat TM, Purpura M, Ziegenfuss TN, Ferrando AA, Arent SM, Smith-Ryan AE, Stout JR, Arciero PJ, Ormsbee MJ, Taylor LW, Wilborn CD, Kalman DS, Kreider RB, Willoughby DS, Hoffman JR, Krzykowski JL, Antonio J. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: protein and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017 Jun 20;14:20. doi: 10.1186/s12970-017-0177-8. PMID: 28642676; PMCID: PMC5477153.
Morton RW, McGlory C, Phillips SM. Nutritional interventions to augment resistance training-induced skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Front Physiol. 2015;6:245.
Schoenfeld BJ, Aragon AA, Krieger JW. The effect of protein timing on muscle strength and hypertrophy: a meta-analysis. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2013;10:53.
Witard OC, Jackman SR, Kies AK, Jeukendrup AE, Tipton KD. Effect of increased dietary protein on tolerance to intensified training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43:598–607.