Live Like an Athlete II – 2024
April 11, 2024
Micronutrients – Vitamin E
April 16, 2024
Live Like an Athlete II – 2024
April 11, 2024
Micronutrients – Vitamin E
April 16, 2024Iron
What is Iron?
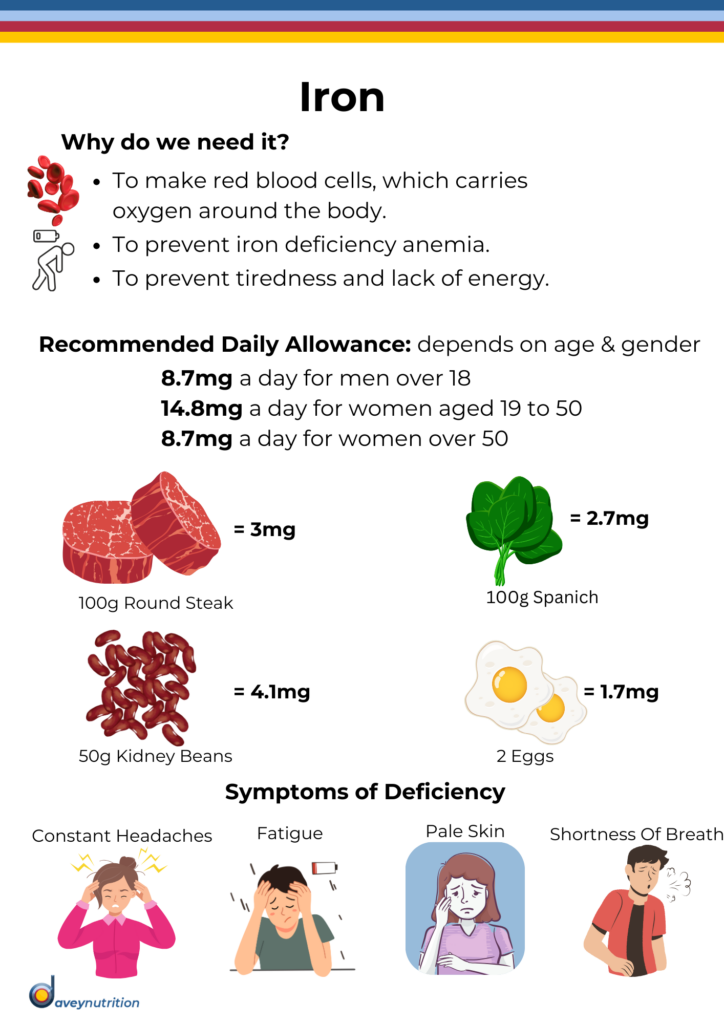
Iron is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. It is a key component of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation.
There are two main types of dietary iron:
- Heme Iron: found in animal products, particularly in red meat, poultry and fish. It is more easily absorbed by the body compared to non-heme iron.
- Non-Heme Iron: present in plant-based foods such as beans, lentils, fortified cereals and some vegetables. It is not as efficiently absorbed by the body as heme iron. However, consuming vitamin C-rich foods along with non-heme iron sources can enhance its absorption.
Why do we need Iron?
- Oxygen Transport: Iron is a vital component of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. Hemoglobin binds with oxygen in the lungs and carries it to tissues and organs.
- Energy Metabolism: Iron is involved in the production of ATP, which is the primary source of energy for cells.
- Immune Function: Iron is involved in the production of white blood cells, which play a key role in defending the body against infections and illnesses.
3 Foods Richest in Iron:
- Liver
- Shellfish (clams, mussels & oysters)
- Legumes & Pulses
Daily Recommended Intake:
For adults, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of Iron varies depending on age and gender:
- Females (19-50): 18mg (due to menstrual losses)
- Females (51+): 8mg
- Males (19+): 8mg
- Pregnant adults (19+): 27mg
Practical Examples:
- Spinach (100g) = 2.7mg of iron.
- Beef Liver (100g) = 6-7mg of iron.
- Chicken Breast (100g) = 0.7mg of iron.
- Chickpeas (100g) = 2.9mg of iron.
- Fortified Breakfast Cereal (30g) = 4-8mg of iron.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy due to the reduced ability of the blood to carry oxygen to body tissues.
- Weakness: physically & mentally.
- Pale Skin.
- Shortness of Breath.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness.
- Brittle Nails.
- Headaches.
Download this factsheet – Iron Factsheet

Want to ensure you’re getting enough Iron in your day? Check out our FREE MEAL PLAN:

Check out our signature Iron recipe here – Chorizo Meatballs
Iron
What is Iron?
Iron is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. It is a key component of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation.
There are two main types of dietary iron:
- Heme Iron: found in animal products, particularly in red meat, poultry and fish. It is more easily absorbed by the body compared to non-heme iron.
- Non-Heme Iron: present in plant-based foods such as beans, lentils, fortified cereals and some vegetables. It is not as efficiently absorbed by the body as heme iron. However, consuming vitamin C-rich foods along with non-heme iron sources can enhance its absorption.
Why do we need Iron?
- Oxygen Transport: Iron is a vital component of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. Hemoglobin binds with oxygen in the lungs and carries it to tissues and organs.
- Energy Metabolism: Iron is involved in the production of ATP, which is the primary source of energy for cells.
- Immune Function: Iron is involved in the production of white blood cells, which play a key role in defending the body against infections and illnesses.
3 Foods Richest in Iron:
- Liver
- Shellfish (clams, mussels & oysters)
- Legumes & Pulses
Daily Recommended Intake:
For adults, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of Iron varies depending on age and gender:
- Females (19-50): 18mg (due to menstrual losses)
- Females (51+): 8mg
- Males (19+): 8mg
- Pregnant adults (19+): 27mg
Practical Examples:
- Spinach (100g) = 2.7mg of iron.
- Beef Liver (100g) = 6-7mg of iron.
- Chicken Breast (100g) = 0.7mg of iron.
- Chickpeas (100g) = 2.9mg of iron.
- Fortified Breakfast Cereal (30g) = 4-8mg of iron.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy due to the reduced ability of the blood to carry oxygen to body tissues.
- Weakness: physically & mentally.
- Pale Skin.
- Shortness of Breath.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness.
- Brittle Nails.
- Headaches.

Download this factsheet – Iron Factsheet

Want to ensure you’re getting enough Iron in your day? Check out our FREE MEAL PLAN:

Check out our signature Iron recipe here – Chorizo Meatballs
Upgrade NOW
Upgrade NOW