Micronutrients – Vitamin D
April 8, 2024
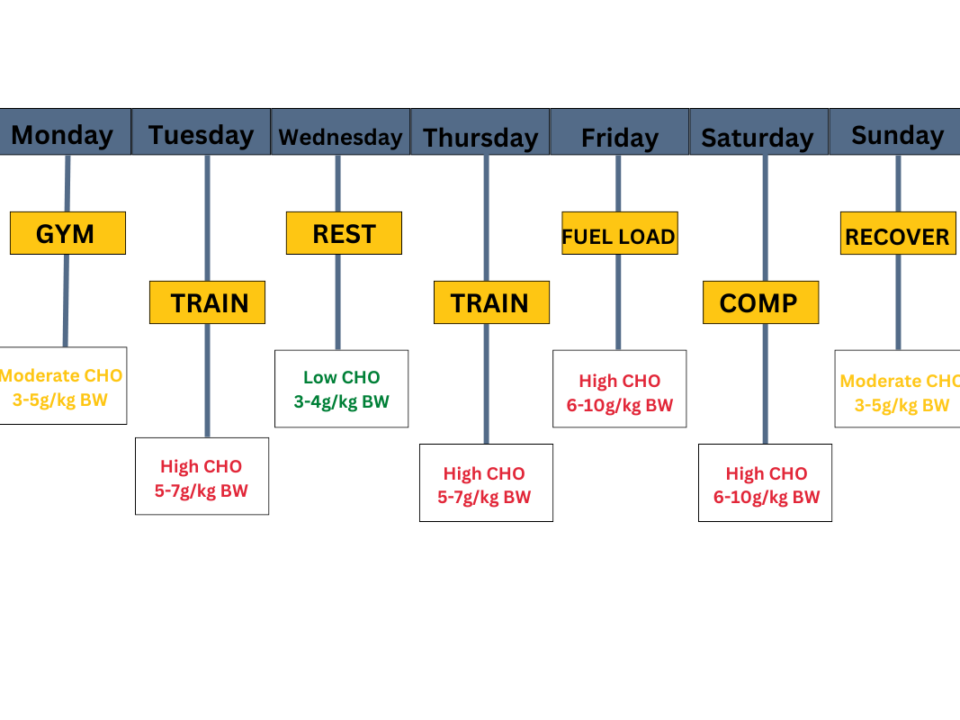
Live Like an Athlete II – 2024
April 11, 2024
Micronutrients – Vitamin D
April 8, 2024
Live Like an Athlete II – 2024
April 11, 2024Omega-3 Fatty Acids
What is Omega-3?
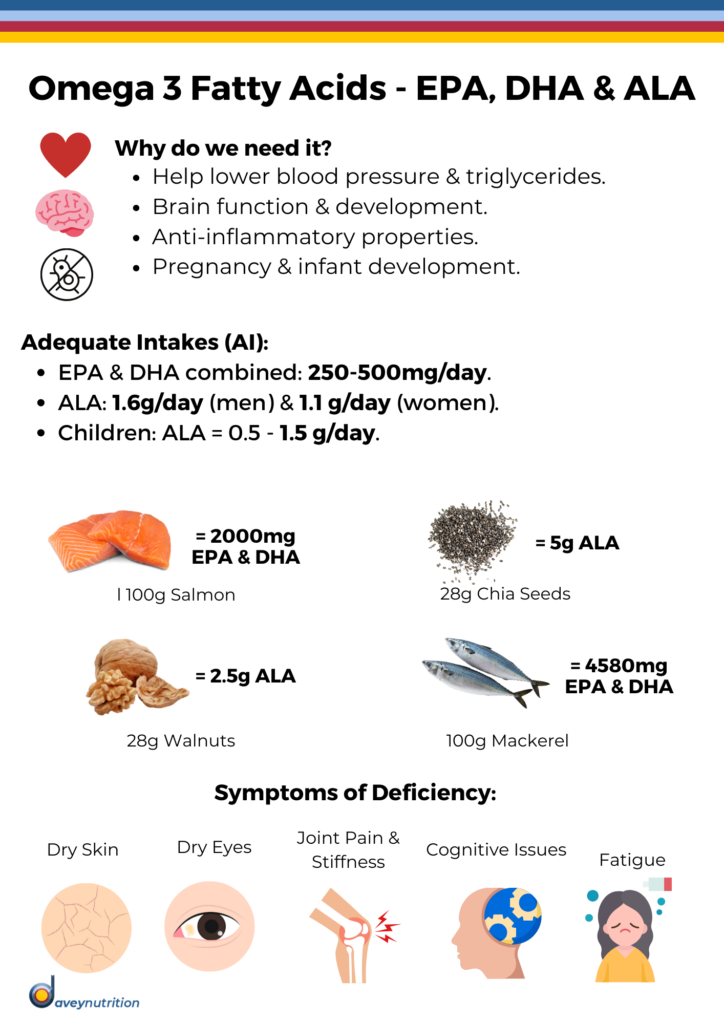
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that are essential, because the body cannot produce them on its own and must obtain them from dietary sources.
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids:
- Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA): ALA is the primary plant-based omega-3 fatty acid found in sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts and hemp seeds.
- Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA): EPA is found in certain types of fatty fish, including salmon, mackerel and sardines. It is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and is associated with cardiovascular health.
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA): DHA is found in fatty fish. It is crucial for brain health and is a major component of the brain and retina.
Why do we need Omega-3’s?
- Heart Health: EPA and DHA have been linked to a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease by helping to lower blood triglycerides, reduce inflammation, and improve blood vessel function.
- Brain Health: DHA, in particular, is crucial for brain development and cognitive function.
- Joint Health: Omega-3s may have anti-inflammatory effects that can benefit joint health.
- Eye Health: DHA is a major component of the retina.
3 Foods Richest in Omega-3’s?
- Fatty Fish (Salmon, mackerel & sardines)
- Chia Seeds & Flax Seeds
- Walnuts
Daily Recommended Intake:
For adults, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of Omega-3 is ~500 milligrams per day.
Practical Examples:
- Walnuts (28 grams) = 250mg of ALA
- Fatty Fish (100g):
- Salmon = ~150mg (combined EPA & DHA)
- Mackerel = ~350mg (combined EPA & DHA)
- Sardines = ~150mg (combined EPA & DHA)
- Chia Seeds (28g) = 490mg of ALA
- Flaxseeds (1tbsp) = 160mg of ALA
Symptoms of Omega-3 Deficiency:
- Dry Skin.
- Brittle Nails.
- Fatigue.
- Joint Pain: deficiency might contribute to increased inflammation, leading to joint pain and stiffness.
- Poor Concentration: may impact cognitive function, including concentration and memory.
Download this factsheet – Omega-3 FA Factsheet

Want to ensure you’re getting enough Omega-3 in your day? Check out our FREE MEAL PLAN:

Check out our signature Omega-3 recipe here – Apple Pie Overnight Oats
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
What is Omega-3?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that are essential, because the body cannot produce them on its own and must obtain them from dietary sources.
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids:
- Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA): ALA is the primary plant-based omega-3 fatty acid found in sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts and hemp seeds.
- Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA): EPA is found in certain types of fatty fish, including salmon, mackerel and sardines. It is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and is associated with cardiovascular health.
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA): DHA is found in fatty fish. It is crucial for brain health and is a major component of the brain and retina.
Why do we need Omega-3’s?
- Heart Health: EPA and DHA have been linked to a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease by helping to lower blood triglycerides, reduce inflammation, and improve blood vessel function.
- Brain Health: DHA, in particular, is crucial for brain development and cognitive function.
- Joint Health: Omega-3s may have anti-inflammatory effects that can benefit joint health.
- Eye Health: DHA is a major component of the retina.
3 Foods Richest in Omega-3’s?
- Fatty Fish (Salmon, mackerel & sardines)
- Chia Seeds & Flax Seeds
- Walnuts
Daily Recommended Intake:
For adults, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of Omega-3 is ~500 milligrams per day.
Practical Examples:
- Walnuts (28 grams) = 250mg of ALA
- Fatty Fish (100g):
- Salmon = ~150mg (combined EPA & DHA)
- Mackerel = ~350mg (combined EPA & DHA)
- Sardines = ~150mg (combined EPA & DHA)
- Chia Seeds (28g) = 490mg of ALA
- Flaxseeds (1tbsp) = 160mg of ALA
Symptoms of Omega-3 Deficiency:
- Dry Skin.
- Brittle Nails.
- Fatigue.
- Joint Pain: deficiency might contribute to increased inflammation, leading to joint pain and stiffness.
- Poor Concentration: may impact cognitive function, including concentration and memory.

Download this factsheet – Omega-3 FA Factsheet

Want to ensure you’re getting enough Omega-3 in your day? Check out our FREE MEAL PLAN:

Check out our signature Omega-3 recipe here – Apple Pie Overnight Oats
Upgrade NOW
Upgrade NOW